- World Population Review Newsletter
- Posts
- Who’s Next to Black Out? The Global Power Crisis
Who’s Next to Black Out? The Global Power Crisis
Grid failures, rising demand, and the nations nearing collapse.
Greetings, vigilant navigator of an electrified world.
The lights are still on—for now. But behind the hum of modern life, power grids are straining. Demand is spiking. Infrastructure is aging. And in some countries, blackouts aren’t coming—they’re already here.
Who’s next? And what does that mean for where you live, invest, or plan your future?
Let’s find out.
Learn how to make every AI investment count.
Successful AI transformation starts with deeply understanding your organization’s most critical use cases. We recommend this practical guide from You.com that walks through a proven framework to identify, prioritize, and document high-value AI opportunities.
In this AI Use Case Discovery Guide, you’ll learn how to:
Map internal workflows and customer journeys to pinpoint where AI can drive measurable ROI
Ask the right questions when it comes to AI use cases
Align cross-functional teams and stakeholders for a unified, scalable approach
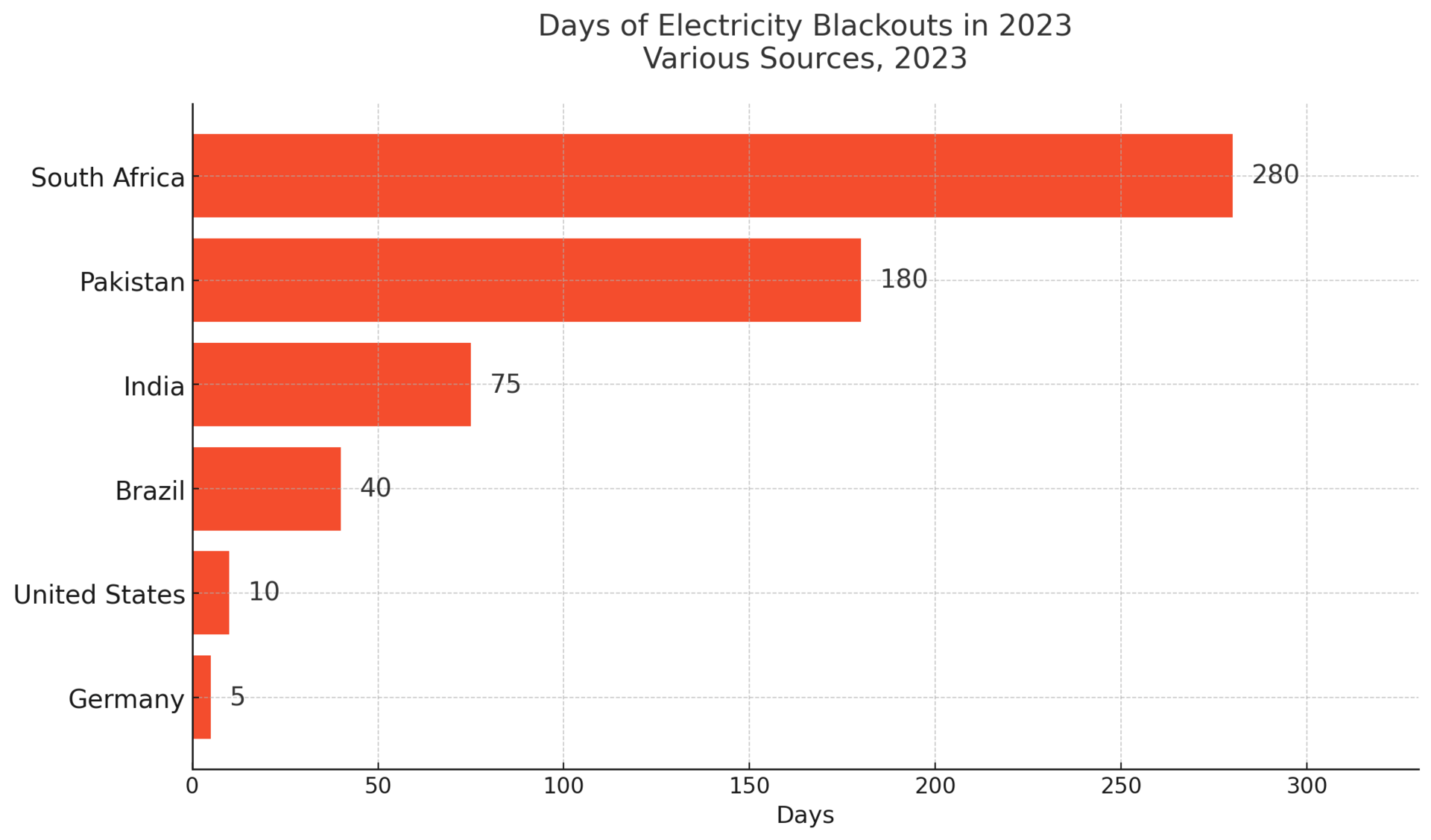
Once hailed as Africa’s industrial powerhouse, South Africa now serves as a global warning. Daily blackouts, known locally as load shedding, have crippled economic growth and eroded public trust. What went wrong?
At the heart lies Eskom, the national utility giant, plagued by aging coal plants, underinvestment, and corruption scandals. While renewable energy projects are underway, they’ve been too slow to counteract decades of mismanagement.
And the effects aren’t abstract—businesses are closing early, students study by candlelight, and hospital operations hang in the balance.
🔎 Did you know? In 2023, South Africa endured more than 280 days of rolling blackouts, the worst in its history—costing the economy over $50 million per day in lost productivity.
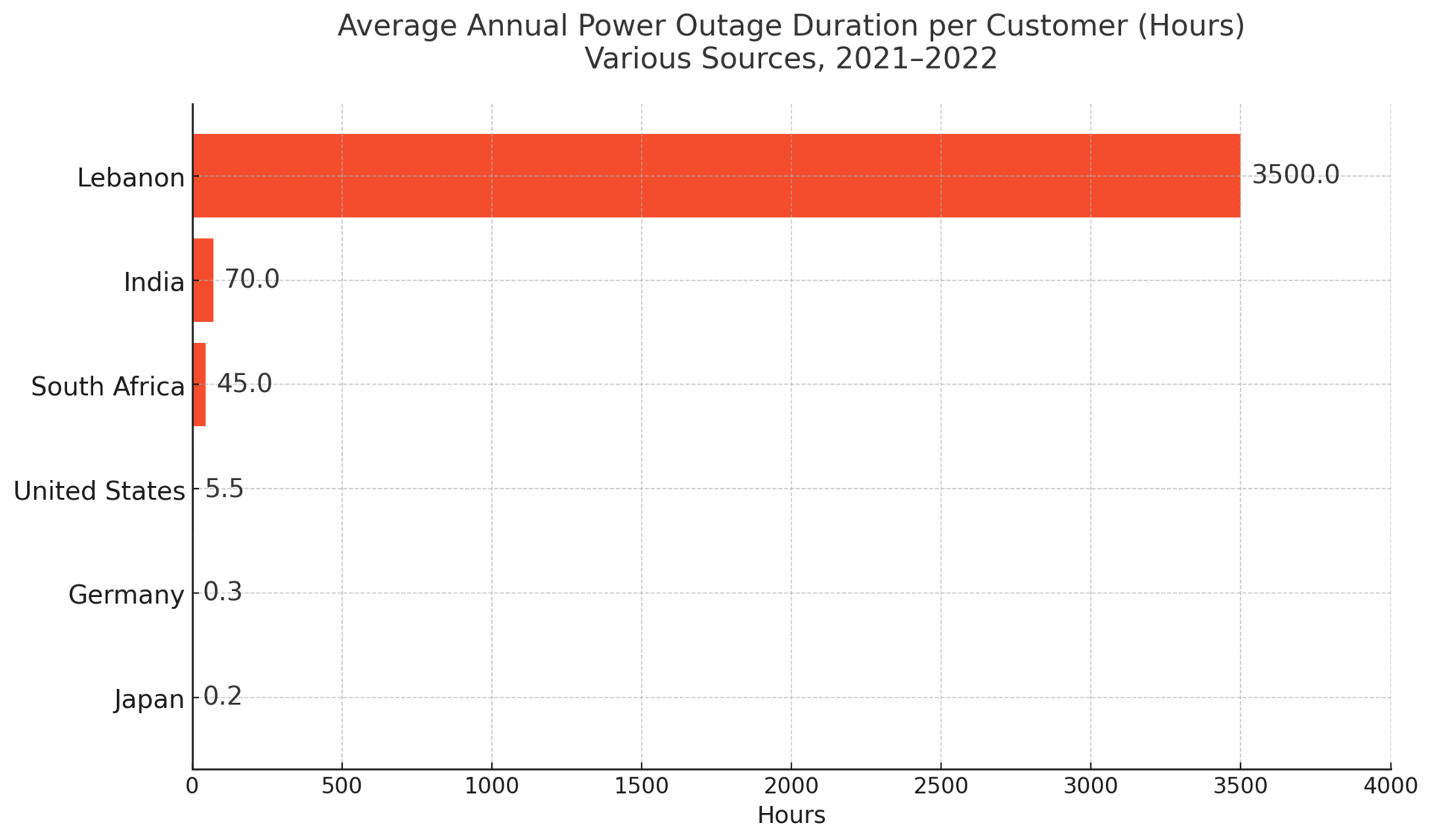
America’s power grid is a marvel—if you’re in the right zip code. But beneath the surface lies a fragmented, overstressed system, especially vulnerable to extreme weather.
The Texas freeze of 2021 exposed how deregulation and lack of interconnection can devastate even energy-rich states. Meanwhile, California continues to face summer blackouts driven by wildfires, heatwaves, and energy transitions.
The real kicker? While demand is skyrocketing—especially from AI data centers and EV charging—investment in grid modernization remains sluggish.
🔎 Unexpected fact: U.S. electricity demand is expected to grow 20% by 2030, but more than 70% of its grid infrastructure is over 25 years old.
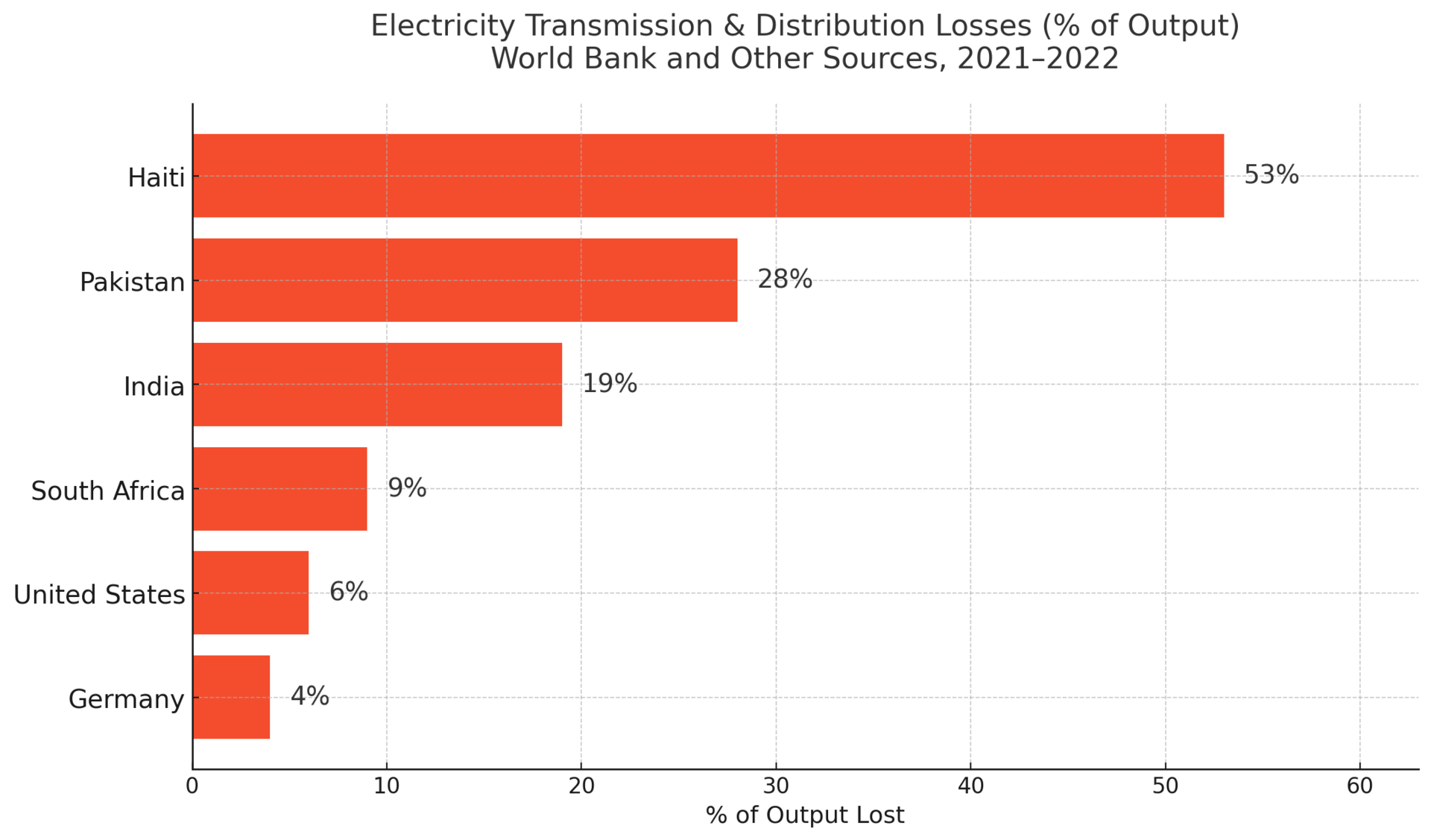
Pakistan’s energy woes are deep and cyclical. Frequent blackouts—sometimes lasting over 12 hours—are now a routine part of life. In early 2023, a nationwide outage left 220 million people without power after a grid failure.
The causes? Outdated infrastructure, crippling debt to energy producers, and political instability. Despite massive hydro and solar potential, development is throttled by policy gridlock and lack of foreign investment.
For a country striving to grow its economy and stabilize its politics, power unreliability poses a core threat to national security.
🔎 Powerful insight: In 2022, nearly one-third of Pakistan’s electricity supply was lost in transmission—enough to power a medium-sized country.
The best marketing ideas come from marketers who live it. That’s what The Marketing Millennials delivers: real insights, fresh takes, and no fluff. Written by Daniel Murray, a marketer who knows what works, this newsletter cuts through the noise so you can stop guessing and start winning. Subscribe and level up your marketing game.
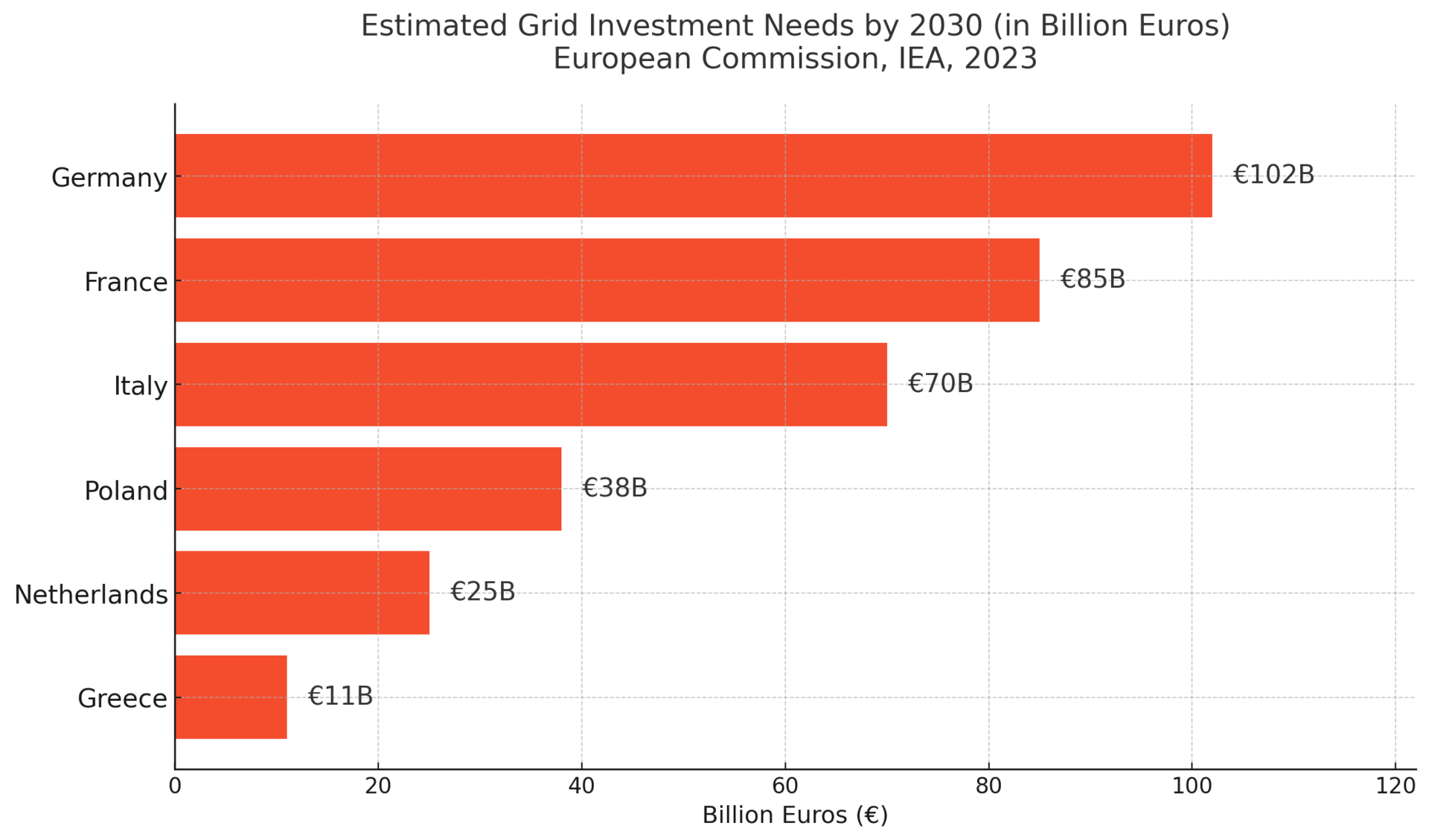
Europe’s energy security has come under intense pressure since the war in Ukraine, particularly in countries dependent on Russian gas. While the continent managed to avoid full-scale blackouts last winter, risks remain.
Countries like 🇩🇪 Germany, 🇵🇱 Poland, and 🇨🇿 the Czech Republic are racing to transition off fossil fuels—but grid reliability is becoming a central challenge. Aging nuclear fleets, lack of storage for renewables, and cross-border transmission limits could turn a harsh winter into a regional crisis.
🔎 Stat to know: The EU needs to invest €584 billion in grid upgrades by 2030 to meet its clean energy goals and prevent widespread outages.
India is the world’s third-largest electricity consumer—and its appetite is growing faster than its grid can handle. During summer 2022, peak power demand hit over 200 GW, leading to massive outages in major cities.
Rural areas fare even worse, with some villages receiving electricity just a few hours a day. The reasons? Coal shortages, bureaucratic bottlenecks, and slow deployment of renewables. The government is investing heavily, but distribution inefficiencies remain a bottleneck.
🔎 Trend alert: India’s energy demand is projected to double by 2040—but nearly 1 in 5 households still face unreliable electricity today.
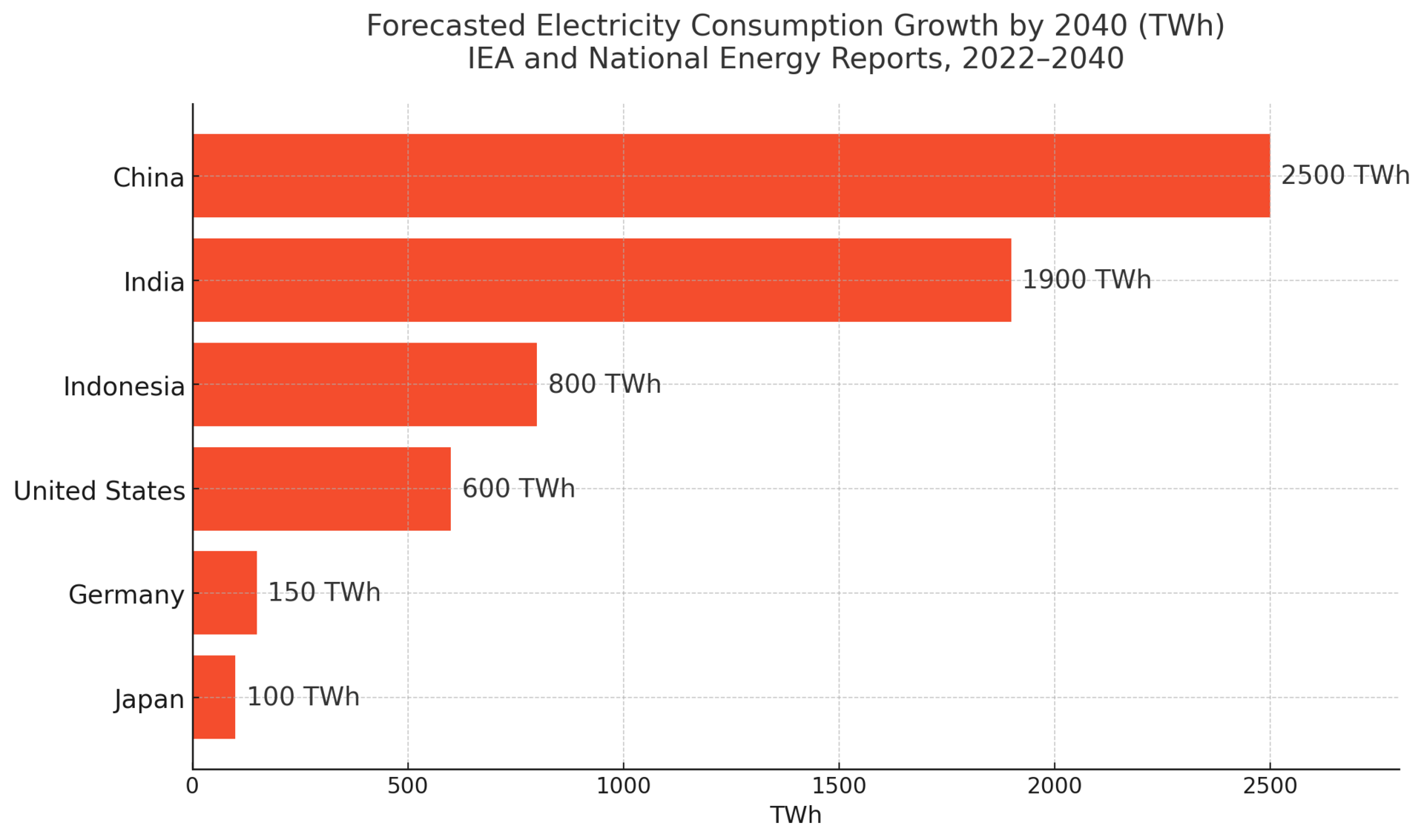
From 🇲🇽 Mexico to 🇧🇷 Brazil to 🇦🇷 Argentina, much of Latin America faces a dual threat: infrastructure that hasn’t kept up with economic growth, and rising climate risks.
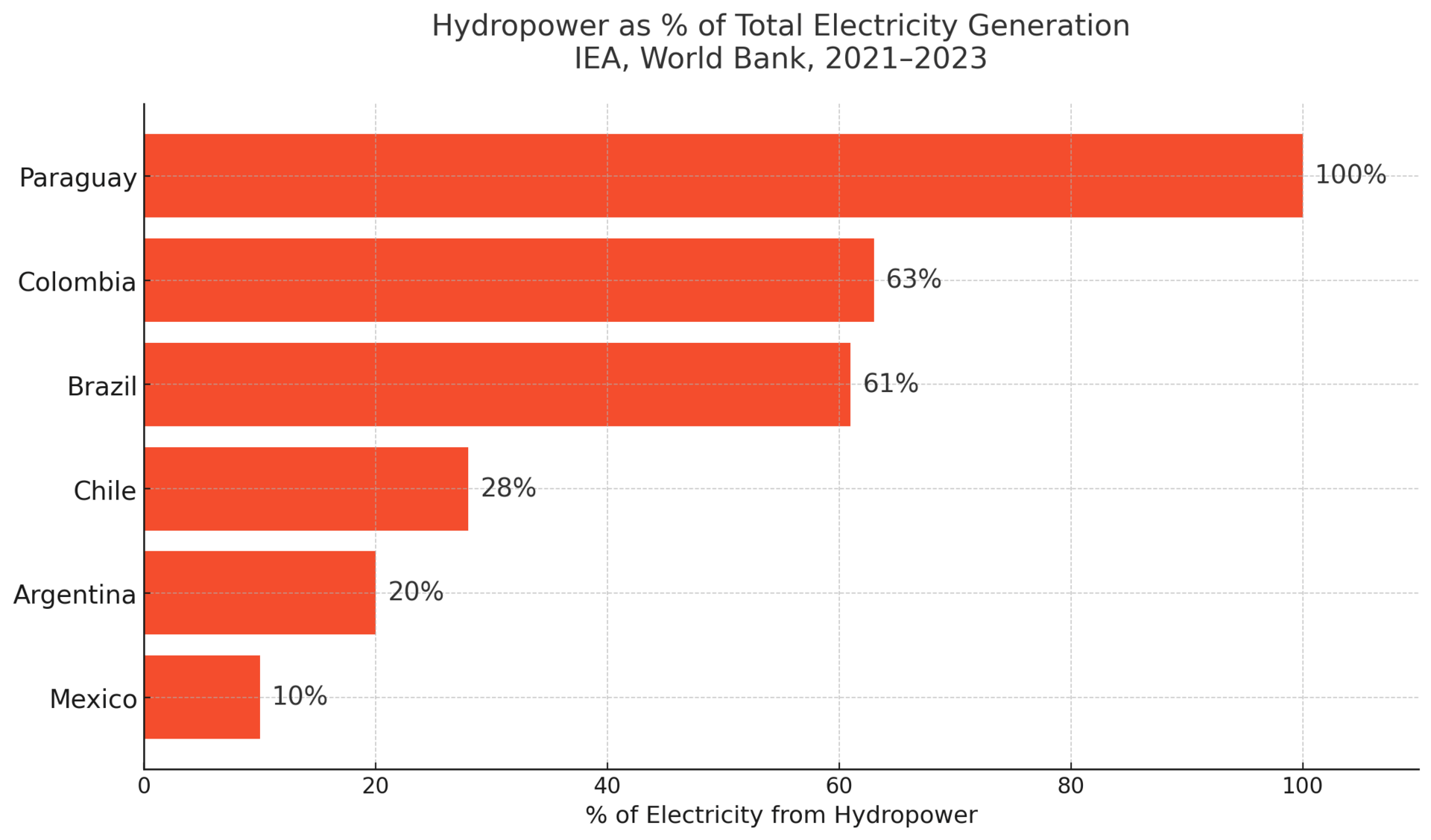
In Brazil, hydroelectric droughts have triggered rolling blackouts. In Argentina, political turmoil disrupts energy reform. Even 🇨🇱 Chile—once seen as a clean energy leader—has faced energy insecurity due to transmission bottlenecks between solar-rich deserts and urban demand centers.
🔎 Little-known fact: Brazil gets over 60% of its electricity from hydropower—but climate change is drying up reservoirs, forcing emergency fossil fuel use.
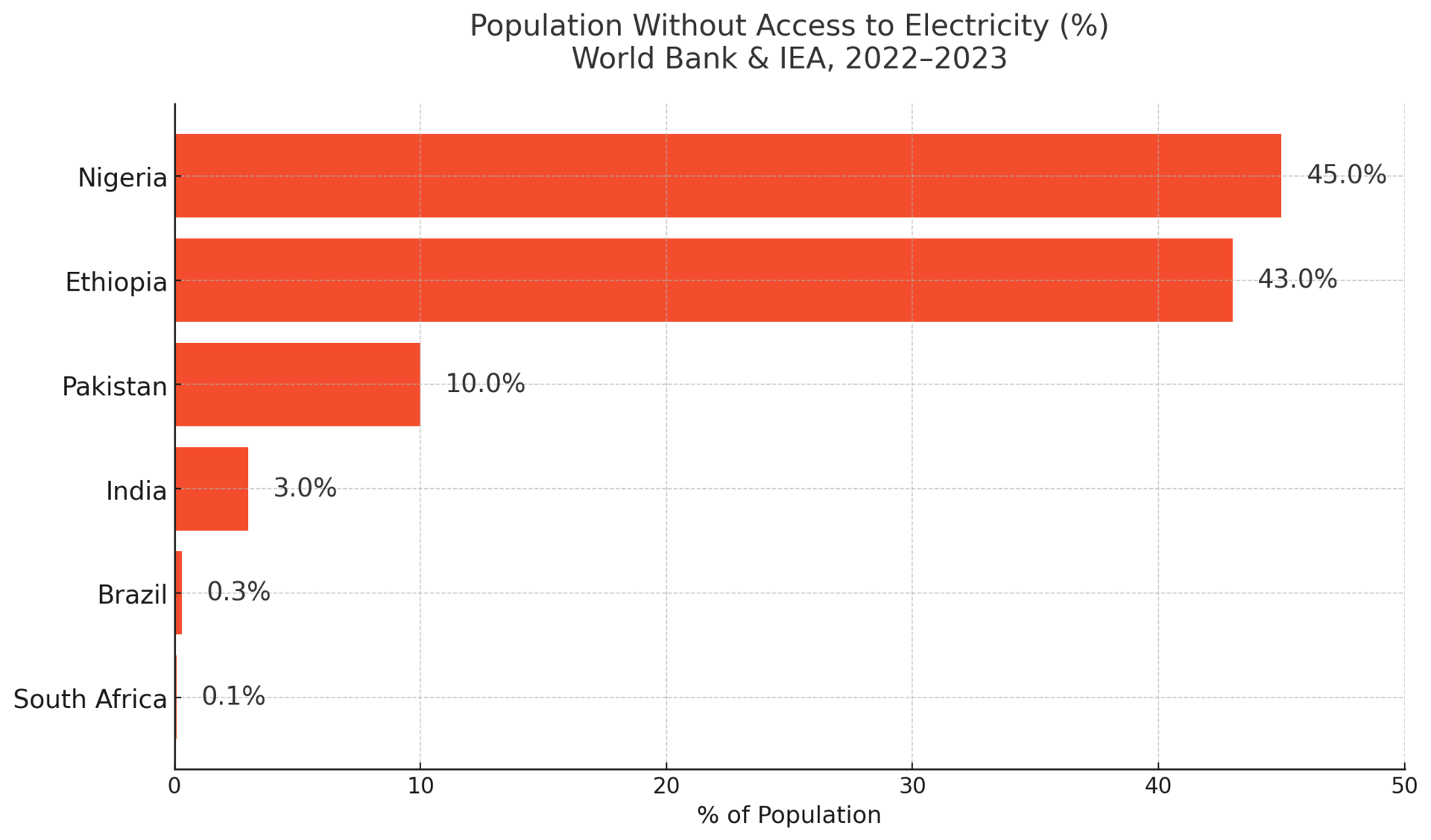
Africa’s most populous nation has immense energy potential—solar, gas, and hydro abound. Yet Nigeria remains chronically underpowered. The national grid collapsed at least four times in 2023 alone.
As a result, more than 85 million Nigerians live without access to electricity. Many rely on expensive, polluting diesel generators, hampering economic development and fueling inequality.
While off-grid solar startups show promise, they are far from filling the gap left by a failing grid system.
🔎 Sobering stat: Nigeria loses an estimated $29 billion annually due to power outages—nearly 5% of its GDP.
Blackouts aren’t just flickers in the dark—they’re signals.
Signals of crumbling infrastructure, policy failure, and widening inequality. From South Africa to Texas to Lagos, the grid is becoming a mirror of how well—or how poorly—a nation can plan for the future.
If you’re thinking about where to live, invest, or simply stay powered on, energy reliability isn’t a footnote. It’s a forecast.
Until next time—stay sharp, stay charged, and stay curious.
Warm regards,
Shane Fulmer
Founder, WorldPopulationReview.com
P.S. Want to sponsor this newsletter? Reach 147,000+ global-minded readers — click here!


